
Volume to weight, weight to volume and cost conversions for Refrigerant R-422D, liquid (R422D) with temperature in the range of -51.12☌ (-60. Calculate how much of this gravel is required to attain a specific depth in a cylindrical, quarter cylindrical or in a rectangular shaped aquarium or pond Substrate, Clay/Laterite weighs 1 019 kg/m³ (63.61409 lb/ft³) with specific gravity of 1.019 relative to pure water. List of these foods starting with the highest contents of Vitamin E (label entry primarily) and the lowest contents of Vitamin E (label entry primarily) Gravels, Substances and Oils A sample of gas contains 2.5 moles of oxygen (02) at STP. A sample of nitrogen gas with an initial pressure of 780 mmHg at -75.0 deg C is heated to 28.0 deg C STP and molar volume 1. A gas with an initial pressure of 1.20 atm at 75.0 Deg C is cooled to -32.0 deg C. ICE CREAM, UPC: 717544301318 weigh(s) 135 grams per metric cup or 4.5 ounces per US cup, and contain(s) 203 calories per 100 grams (≈3.53 ounces) Ĩ1 foods that contain Vitamin E (label entry primarily). Calculate the final pressure in atm for each of the following conditions: a.

759 through 858 millimeters of mercury to atmospheres conversion cards remember that p H/p tot=n H/n tot=v h/v tot so the mole ratio of hydrogen to the mixture is is.total pressure is 2 atm Flourine+.5 atm Hydrogen=2.5 atm total.P nitrogen=3.61 atm total-1.20 atm Oxygen=2.41 atm Nitrogen.P A/P tot=n A/N tot can be rearranged to P A=(P tot)(n A/N tot) to find the partial pressures.5) A 500.0 mL sample of O2(g) is at 780 mmHg and 30C.
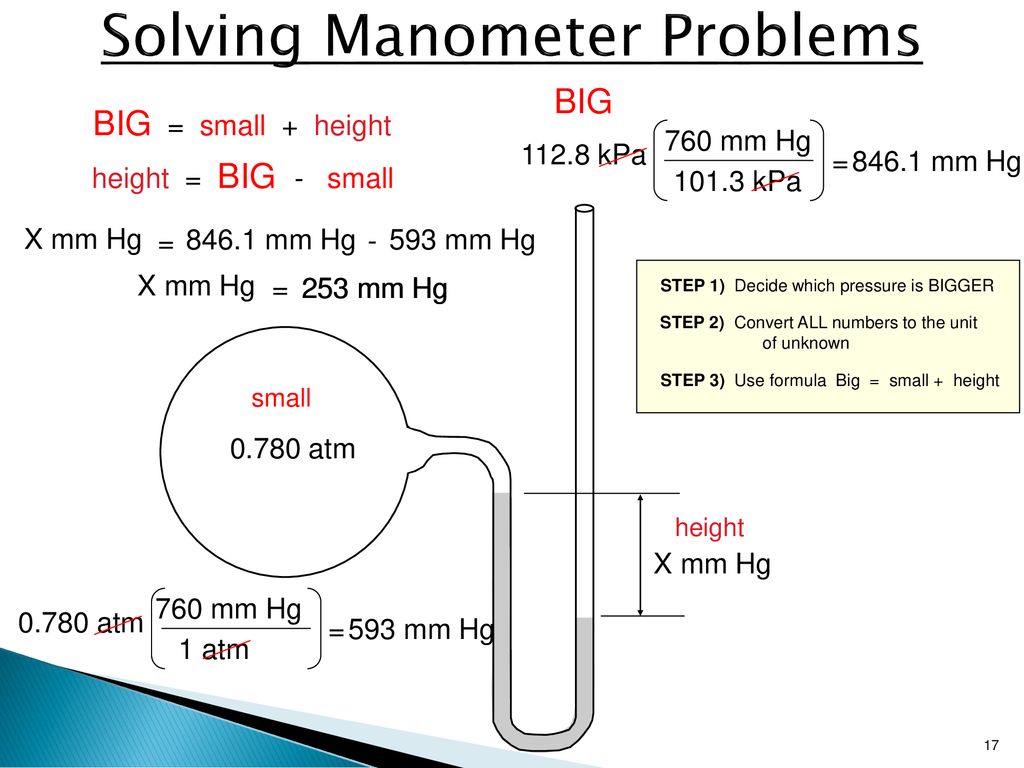
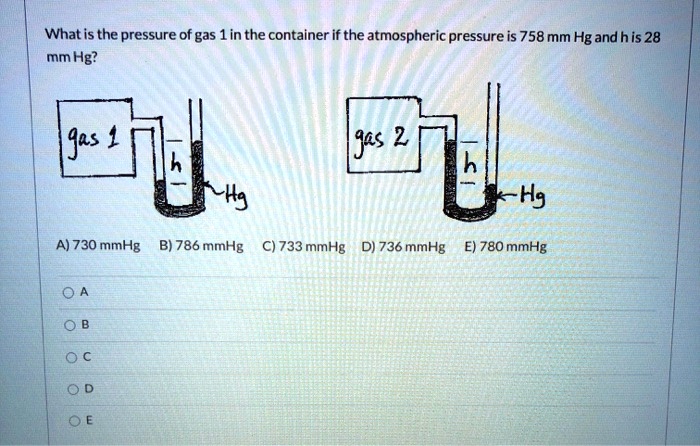
The law of partial pressures also applies to the total number of moles if the other values are constant, soĤ mol Hydrogen+8 mol Oxygen+12 mol Helium+6 mol Nitrogen= 30 moles total



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
